Quality in, quality out. It’s a fundamental project management concept that takes practice when applied to real-world situations.
For starters, project managers must understand what quality looks like. Then, they need to know which processes will produce these high-quality outcomes.
It takes patience and strong organizational skills to deliver top-tier results. But by practicing effective project quality management (PQM), managers can boost their output to delight clients and stakeholders alike.
What’s project quality management?
PQM is a set of processes designed to improve the entire project life cycle, from ideation to planning to implementation. This structured approach involves continuously evaluating and optimizing tools, workflows, and standard procedures to create a final output that’s as high-quality as possible.
Whether clients have specific demands or shareholders have mandatory criteria, quality management in project management is the secret to turning a good project into a great one.
Why is project quality management important?
PQM is a must-have for any team that wants to exceed project expectations. And as part of the strategic planning process, PQM also ensures that the project aligns with broader organizational goals.
Here are a few more benefits of having a PQM process:
- Improved customer satisfaction: Everyone loves high-quality products and services, so ensuring you exceed expectations means customers are more than satisfied.
- Reduced costs: Identifying and resolving issues early on curtails the high prices that could arise if problems are discovered later.
- Increased efficiency: A robust quality management system helps streamline processes, reduce waste, and ensure optimal resource use.
- Risk mitigation: Regularly checking the quality of a project helps identify risks early and address them before they become significant issues.
- Enhanced reputation: When your team delivers high-quality results, you’re bound to turn some heads. Consistently overachieving on outcomes enhances your reputation in the market, making you a go-to choice for future projects.
What’s a quality management plan?
A quality management plan (QMP) is the guide project managers create and use for implementing their PQM approach. This document outlines how the team will meet the quality requirements set by the client or other key stakeholders.
A QMP rests on three main processes:
- Quality planning: You identify the project’s critical quality requirements and how your team will meet them.
- Quality assurance: Throughout project execution, you check in on your project’s health to ensure that your team follows the right processes and seeks ways to further deliver customer value.
- Quality control: Quality process management involves monitoring and recording the results of quality-focused activities to assess performance and recommend necessary changes. At this point, you discover if the output quality is up to par, and if it’s not, you figure out what needs tweaking.
Key elements of project quality management
Managing project quality typically involves the following elements:
- Performance measurement: Collecting and analyzing data to evaluate performance is vital to PQM. This involves setting performance benchmarks and comparing results against them. You might use performance measurement tools such as key performance indicators (KPIs), balanced scorecards, or quality scorecards to conduct this work.
- Preventive action: Prevention is typically better than fixing active issues, saving teams time and frustration in the long run. Being proactive might involve regular quality audits, risk assessments, or implementing a change management process.
- Continuous improvement: The quest for quality is never-ending — it’s a constant cycle of measuring, analyzing, and improving. This improvement process involves regularly reviewing performance metrics, seeking feedback, and implementing improvements.
9 steps for implementing project quality management
Implementing PQM is a systematic process that requires careful planning, execution, and monitoring. Here’s a nine-step guide to carry you through all three phases.
1. Define quality objectives
Clearly outline what “quality” means for your project, engaging with consumer experts for insights about which parameters will add the most value. Use these insights to define performance metrics, client satisfaction markers, and specific deliverable standards that align with the overall operational plan.
2. Select relevant quality tools and techniques
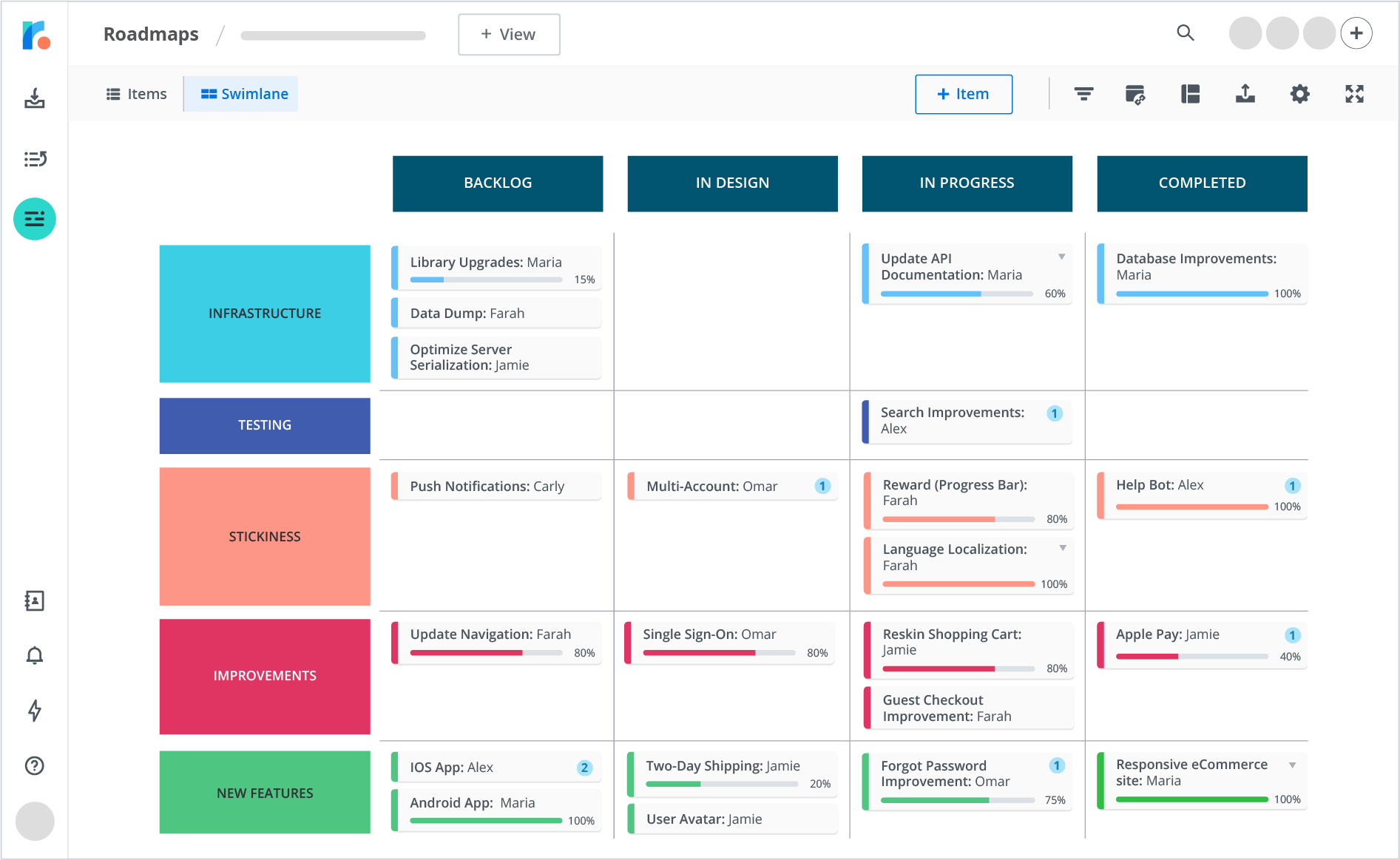
Based on the nature and scope of your project, choose the appropriate quality management tools, such as matrix diagrams, flowcharts, or roadmaps. These play an instrumental role in monitoring tasks as they move from the backlog to completion. Ensure that your team is trained and comfortable using these tools.
3. Develop a quality management plan
Detail how you’ll achieve quality objectives, including processes for quality assurance, quality control, and continuous improvement. Clearly define roles and responsibilities related to quality management and incorporate a review mechanism within your QMP for timely evaluations and updates.
4. Engage stakeholders
Regularly communicate with stakeholders about quality expectations and updates, scheduling briefings, standups, and workshops to keep everyone on the same page regarding expectations.
For more detailed updates and effective planning adjustments, use surveys and one-on-one interviews to gather feedback and ensure the project remains aligned with quality objectives.
5. Monitor and measure quality
Use previously selected tools to continuously monitor project performance against set quality benchmarks. Regularly review KPIs, scorecards, and other chosen metrics. You might also build visual aids like dashboards for a quick snapshot of your quality metrics.
6. Implement corrective and preventive actions
Set up continuous feedback loops to proactively identify issues. This involves taking a regular team pulse and keeping your ears open to negative feedback. And when you notice discrepancies between expected and actual performance, identify root causes and implement corrective actions to address current and prevent future issues.
7. Review and adjust
Periodically review the QMP to ensure it remains relevant and practical. Adjust strategies and processes based on feedback, lessons learned, and changing project dynamics. And consider implementing quarterly reviews or meetings after significant milestones to collect actionable team and customer feedback.
8. Celebrate quality achievements
Recognize and reward team members for achieving quality milestones — bonuses, public recognition, and even simple thank-you notes make a difference. These gestures foster a culture of quality and motivate the team to maintain high standards.
9. Conduct a post-project quality review
After project closure, review the overall performance of your quality-focused initiatives. Document lessons learned, best practices, and areas for improvement to inform future projects. And to get the most from your review sessions, facilitate an environment that encourages open, honest feedback from the entire team.
7 quality management tools
The best PQM process starts with high-quality tools. Consider adding any or all of these into your workflow.
1. Matrix diagram
A matrix diagram is a visual tool that displays the relationship between different data sets. Comparing rows and columns of data against each other quickly uncovers dependencies and roadblocks, helping managers identify patterns, correlations, and inconsistencies for data-driven decision making.
2. Affinity diagram
This diagram organizes large amounts of data into groups based on dataset relationships. At first, the information may seem unrelated, but the affinity diagram sorts it by themes to find hidden dependencies. It’s beneficial when dealing with complex problems that involve multiple datasets.
3. Interrelationship diagram
An interrelationship diagram showcases the cause-and-effect relationships among different project aspects, which can help managers identify an issue’s root cause and potential consequences.
4. Network diagram
These diagrams show a project’s tasks and dependencies. Managers use them to better understand task sequencing, which helps when scheduling and allocating resources. And you might also use this task dependency outline to identify the project’s critical path and any relevant risks.
5. Prioritization matrix
This chart ranks the importance of different issues based on user-set criteria, like impact and urgency. This information is instrumental in risk management, where managers must allocate resources effectively to minimize delays and incomplete deliverables.
6. Check sheet
This is a simple, structured form for collecting and analyzing data. You might use a check sheet before creating any other matrices or flowcharts, compiling data you can then use to plan projects.
7. Flowchart
Flowcharts visually represent a process, detailing every step involved. A common type is the swimlane diagram, which segments a process into categories to show who’s responsible for tasks. You can use these charts to showcase the most effective workflows teammates ought to follow.

The best tools for project quality management
To offer your team project visibility and easy performance tracking, try Roadmunk by Tempo, an audience-friendly platform that creates customizable project roadmaps. Pair this tool with Timesheets by Tempo to better understand how to improve team performance. Sign up today.









